December 2025
North America News
On 10 November 2025, the United States Environmental Protection Agency released a proposal to make PFAS reporting requirements more practical and implementable, reducing regulatory burden.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is proposing amendments to the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulation related to reporting and recordkeeping requirements for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). As outlined October 2023, the regulation requires manufacturers (including importers) of PFAS in any year between 2011-2022 to report certain data to the EPA regarding exposure and environmental and health effects. On 10 November 2025, the EPA proposed incorporating certain exemptions and other modifications to the scope of the reporting regulation. These proposed changes will reduce unnecessary or potentially repetitious reporting requirements for manufacturers.
The proposed exemptions apply to:
PFAS manufactured (including imported) in mixtures or products at concentrations 0.1% or lower
Imported articles
Certain byproducts (chemical substances produced without a separate intent during the manufacture, processing, use, or disposal of another chemical substance or mixture)
Impurities (chemical substances which are unintentionally present with another chemical substance)
Research and development chemicals
Non-isolated intermediates (any intermediate that is not intentionally removed from the equipment in which it is manufactured. An intermediate is any chemical substance that is partially or fully consumed in chemical reactions used intentionally for the manufacture of other chemical substances or mixtures or is intentionally present for altering the rates of such chemical reactions)
Since promulgating the final rule on 11 October 2023, the EPA has moved the reporting deadline twice. In this proposal, further postponement will be needed.
Chapter 173-337 WAC: Safer Products Restrictions and Reporting on PFAS is amended to establish PFAS prohibitions and mandatory reporting obligations for 12 additional consumer product categories, expanding the regulatory scope to encompass 16 categories total.
On 20 November 2025, The Washington State Department of Ecology amended regulation, Chapter 173-337 WAC: Safer Products Restrictions and Reporting on PFAS, which prohibits intentionally added perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS) and mandates manufacturers to report PFAS in specified product categories. These restrictions and reporting requirements build upon the original regulation enacted in 2023, which addressed intentionally added PFAS in four categories: aftermarket stain- and water-resistant treatments, carpets and rugs, as well as leather and textile furnishings.
Details of the implementation are as follows:
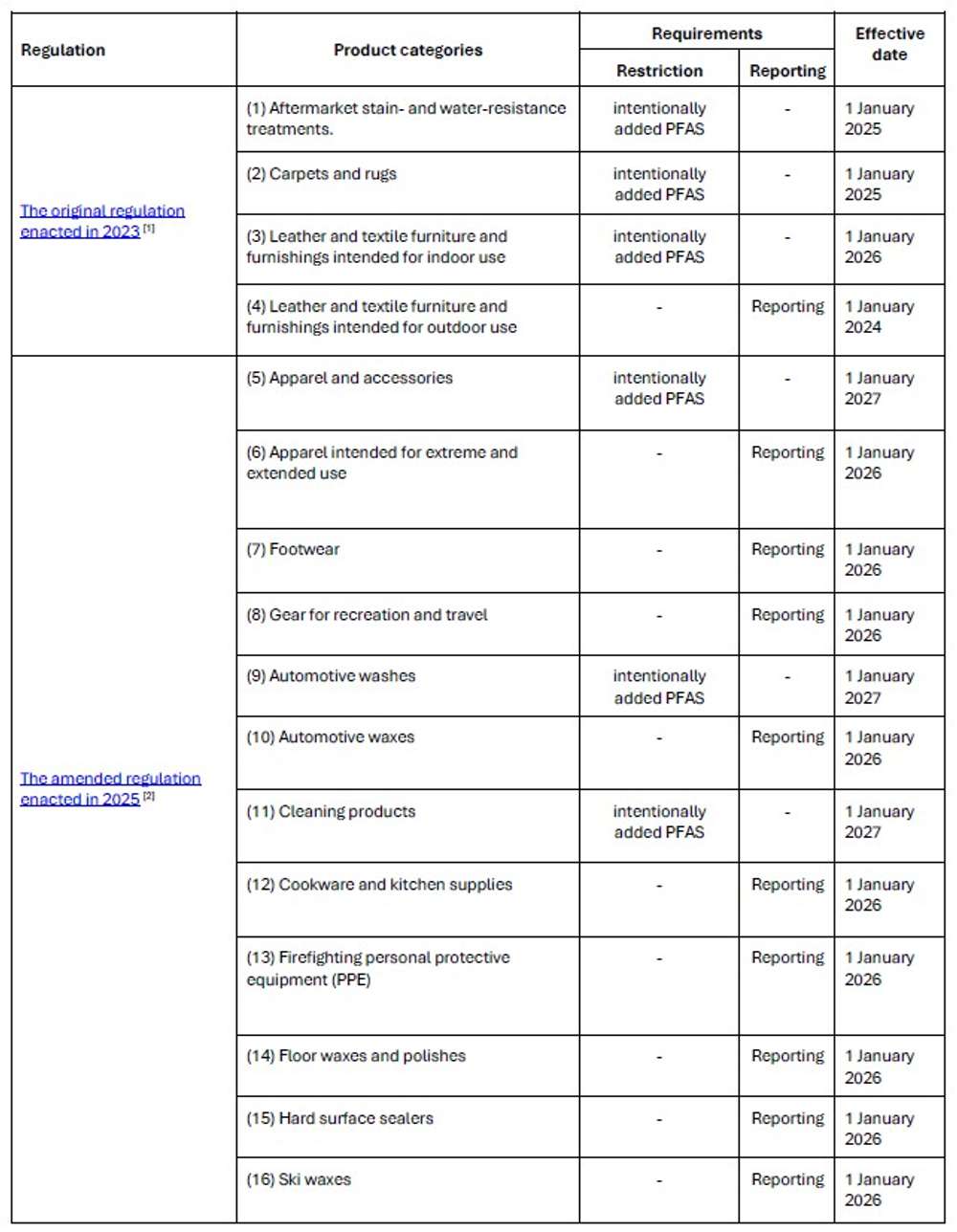
Please note that for the amendments, the reporting period begins on 1 January 2026, with submissions required by 31 January 2027, and recurring annually thereafter. Washington State Department of Ecology presumes the detection of total fluorine above 50 ppm indicates the intentional addition of PFAS; however, manufacturers can rebut this presumption by submitting a statement supported by "credible evidence" that PFAS were not intentionally added to the product.
Europe News
In late November 2025, the EU published three amendments for the RoHS directive for the exemption of lead content in various applications.
On 21 November 2025, the European Union (EU) officially announced three amendments for the update to the exemption of the RoHS directive (Restriction of the use of certain Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic equipment - Directive 2011/65/EU) concerning the use of lead in alloys [Directive (EU) 2025/2364], high-melting-point solders [Directive (EU) 2025/1802], and glass or ceramic components [Directive (EU) 2025/2363].
These amendments shall enter into force 20 days after their official publication (i.e. on 11 December 2025).
These amendments pertain to the exemptions specified in Annex III of Directive 2011/65/EU, including the content in point 6 and point 7. Details of these updates are summarized in the table as below.
Updates for point 6 in Annex III of Directive 2011/65/EU
| Exemption | Scope and dates of applicability | |
|---|---|---|
| 6(a) | Lead as an alloying element in steel for machining purposes and in galvanised steel containing up to 0.35 % lead by weight | Expires on 11 December 2026 |
| 6(a)-I | Lead as an alloying element in steel for machining purposes containing up to 0.35 % lead by weight | Expires on 30 June 2027 for all categories. |
| 6(a)-II | Lead as an alloying element in batch hot-dip galvanised steel components containing up to 0.2 % lead by weight | Expires on 30 June 2027 for all categories. |
| 6(b) | Lead as an alloying element in aluminium containing up to 0.4 % lead by weight | Expires on 11 June 2027 |
| 6(b)-I | Lead as an alloying element in aluminium containing up to 0.4 % lead by weight, provided it stems from lead-bearing aluminium scrap recycling | Expires on 11 December 2026 for categories 1-7, 10. Expires on 30 June 2027 for categories 9 industrial monitoring and control instruments, and 11. |
| 6(b)-II | Lead as an alloying element in aluminium for machining purposes with a lead content up to 0.4 % by weight | Expires on 11 June 2027 for categories 1-7, 10. Expires on 30 June 2027 for categories 9 industrial monitoring and control instruments and 11. |
| 6(b)-III | Lead as an alloying element in aluminium casting alloys containing up to 0.3 % lead by weight provided it stems from lead-bearing aluminium scrap recycling | Expires on 30 June 2027 for categories 1-8, 9 other than industrial monitoring and control instruments, and 10. |
| 6(c) | Copper alloy containing up to 4 % lead by weight | Expires on 30 June 2027. |
Updates for point 7 in Annex III of Directive 2011/65/EU
| Exemption | Scope and dates of applicability | |
|---|---|---|
| 7(a) | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 30 June 2027. |
| 7(a)-I | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) for internal interconnections for attaching die, or other components along with a die in semiconductor assembly with steady state or transient/impulse currents of 0.1 A or greater or blocking voltages beyond 10 V, or die edge sizes larger than 0.3 mm × 0.3 mm | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-II | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) for integral (meaning internal and external) connections of die attach in electrical and electronic components, if all the following conditions are met: — the thermal conductivity of the cured/sintered die-attach material is > 35 W/(m × K), — the electrical conductivity of the cured/sintered die-attach material is > 4.7 MS/m, — solidus melting temperature is higher than 260 °C | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-III | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) in first level solder joints (internal or integral connections – meaning internal and external) for manufacturing components so that subsequent mounting of electronic components onto subassemblies (i.e. modules, sub-circuit boards, substrates, or point-to-point soldering) with a secondary solder does not reflow the first level solder. This sub-entry excludes die attach applications and hermetic sealings | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-IV | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) in second level solder joints for the attachment of components to printed circuit board or lead frames: (1) in solder balls for the attachment of ceramic ball-grid-array (BGA); (2) in high temperature plastic overmouldings (> 220 °C) | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-V | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) as a hermetic sealing material between: (1) a ceramic package or plug and a metal case; (2) component terminations and an internal sub-part | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-VI | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) for establishing electrical connections between lamp components in incandescent reflector lamps for infrared heating, high intensity discharge lamps, or oven lamps | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(a)-VII | Lead in high melting temperature type solders (i.e. lead-based alloys containing 85 % by weight or more lead) for audio transducers where the peak operating temperature exceeds 200 °C | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 24 of this Annex) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(c)-I | Electrical and electronic components containing lead in a glass or ceramic other than dielectric ceramic in capacitors, e.g. piezoelectronic devices, or in a glass or ceramic matrix compound | Applies to all categories and expires on 30 June 2027. |
Updates for point 7 in Annex III of Directive 2011/65/EU (Cont’d)
| Exemption | Scope and dates of applicability | |
|---|---|---|
| 7(c)-II | Lead in dielectric ceramic in capacitors for a rated voltage of 125 V AC or 250 V DC or higher | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by point 7(c)-I or 7(c)-IV) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(c)-V | Electrical and electronic components containing lead in a glass or glass matrix compound that fulfils any of the following functions: (1) for protection and electrical insulation in glass beads of high-voltage diodes and glass layers for wafers; (2) for hermetic sealing between ceramic, metal and/or glass parts; (3) for bonding purposes in a process parameter window for < 500 °C combined with a viscosity of 1 013.3 dPas (‘glass-transition temperature’); (4) for use as a resistive material such as ink, with a resistivity range from 1 ohm/square to 100 megohm/square, excluding trimmer potentiometers; (5) for use in chemically modified glass surfaces for microchannel plates (MCPs), channel electron multipliers (CEMs) and resistive glass products (RGPs). | Applies to all categories and expires on 31 December 2027. |
| 7(c)-VI | Electrical and electronic components containing lead in a ceramic that fulfils any of the following functions: (1) for use in piezoelectric lead zirconium titanate (PZT) ceramics; (2) for providing ceramics with a positive temperature coefficient (PTC). | Applies to all categories (except applications covered by points 7(c)-II, 7(c)-III and 7(c)-IV of this Annex as well as point 14 of Annex IV) and expires on 31 December 2027. |
The European Commission has published Notice C (2025) 7699 on 21 November 2025, providing comprehensive guidelines for businesses on the General Product Safety Regulation (EU) 2023/988. This regulation, effective from 13 December 2024, mandates that only safe products be placed on the market in the European Union (EU). The guidelines detail obligations for economic operators and online marketplaces regarding risk assessment, the mandatory EU "Responsible Person," accident reporting, and specific requirements for distance sales.
The (EU) 2023/988 General Product Safety Regulation (GPSR) repeals Directive 2001/95/EC and establishes a general safety requirement for consumer non-food products. European Commission Notice C (2025) 7699 published on 21 November 2025 clarifies the practical implementation of these rules and details the obligations for economic operators and online marketplaces, as outlined below
1. Scope and General Safety Requirement
The GPSR applies to products placed on the market or offered (including online) from 13 December 2024. Products are presumed safe if they comply with relevant European standards referenced in the Official Journal. In the absence of standards, businesses must perform internal risk assessments taking into account the precautionary principle.
2. Economic Operator Obligations
The guidelines distinguish specific duties for different actors. A single business may fall into multiple categories depending on their function for a specific product.
| Actor | Key Obligations |
| Manufacturer | Conduct internal risk analysis. Create technical documentation (retain for 10 years). Ensure product traceability and safety labeling. |
| Importer | Verify manufacturer compliance. Add importer contact details to product/packaging. Ensure storage or transport does not affect product safety and labelling. |
| Distributor | Verify compliance of manufacturer and importer markings. Cooperate with recalls. |
| Responsible Person (EU) | Mandatory for all products. Must hold technical documentation and cooperate with authorities. |
3. Online Marketplaces & Distance Sales
Online Marketplaces: Must register on the Safety Gate Portal, designate a single point of contact for authorities, and process takedown orders within two working days.
Distance Sales Offers: Must visibly display the manufacturer's name/contact, the Responsible Person's details (if manufacturer is non-EU), a product picture/identifier, and warnings.
4. Accident Reporting and Recalls
Businesses must report accidents resulting in death or serious health effects via the Safety Business Gateway. In the event of a recall, consumers must be offered at least two remedies (repair, replacement, or refund), unless it is not possible or is disproportionate. In this case, one remedy should be offered.
Subscribe to our Regulatory Updates
Unsubscribe at any time. Read our privacy policy.